When it all goes wrong Mutations Chapter 12 Section 4 Biology Diagrams This review focuses on recent progress in understanding non-random chromosome segregation errors in mammalian cells. We discuss the current evidence for non-random chromosome segregation errors in mitosis and meiosis and its various proposed causes. Here, we reveal that CENP-E haploinsufficiency results in chromosome misalignment, spindle disorganization, and metaphase arrest in spermatogonia, which leads to the loss of spermatogonia, chromosomal instability, and spermatogenic disorders. Here, we find that the misalignment of chromosomes caused by Spindly depletion is directly provoking spindle misorientation. Chromosome misalignments induced by CLIP‐170 or CENP‐E depletion or by noscapine treatment are similarly accompanied by severe spindle‐positioning defects.
+Mistakes+with+a+Portion+of+a+Chromosome.jpg)
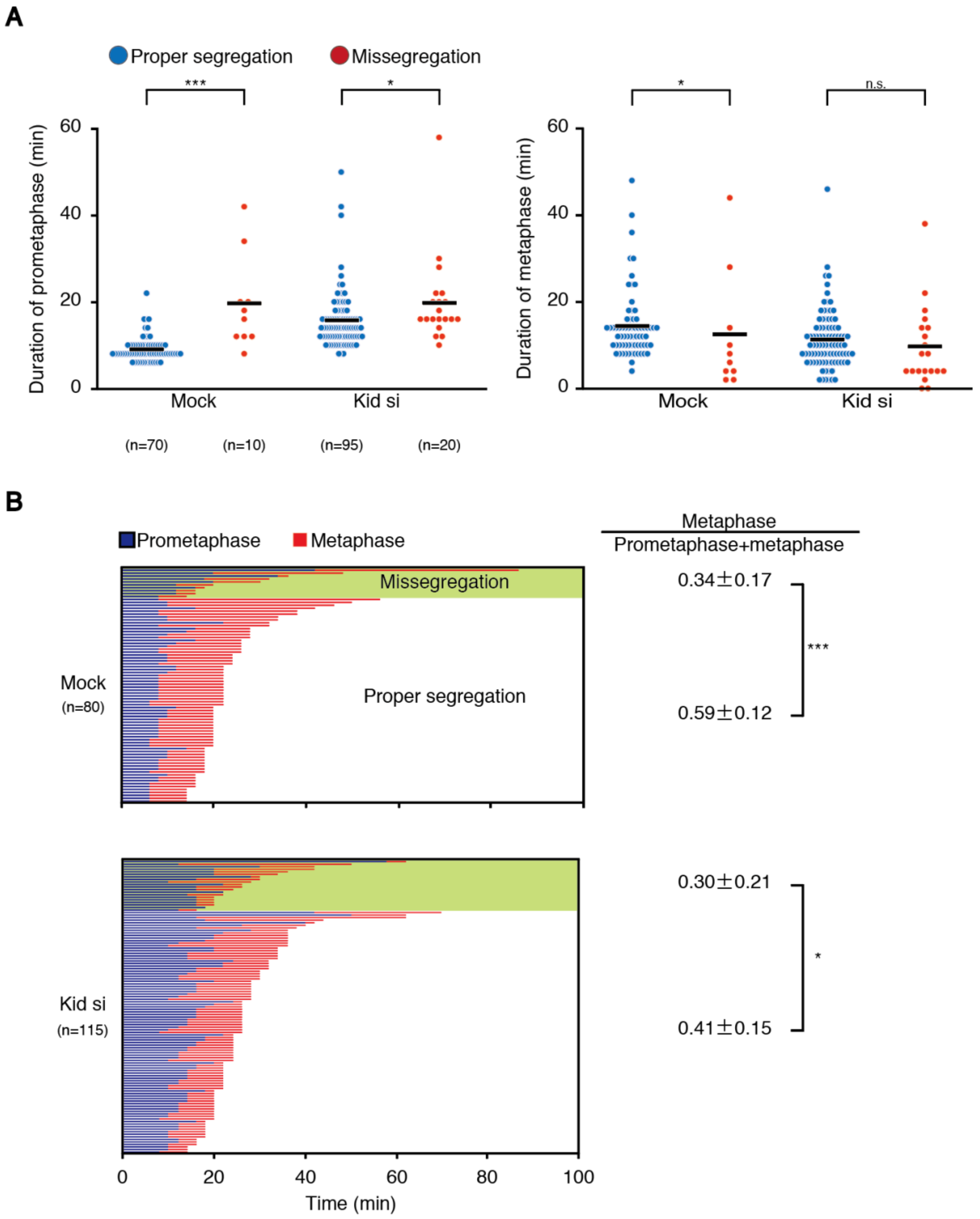
Here, we show that premature peripheral spindle positioning causes abnormal kinetochore-microtubule (K-MT) attachments, chromosome misalignment, aneuploidy, and impaired early embryonic development. Chromosomal instability (CIN), the persistent reshuffling of chromosomes during mitosis, is a hallmark of human cancers that contributes to tumor heterogeneity and has been implicated in driving metastasis and altering responses to therapy. Though multiple mechanisms can produce CIN, lagging chromosomes generated from abnormal merotelic attachments are the major cause of CIN in a variety of Here, we addressed whether delayed chromosome alignment to the spindle equator increases the rate of chromosome missegregation. Cancer cell lines depleted of Kid, a chromokinesin involved in chromosome congression, showed chromosome alignment with a slight delay, and increased frequency of lagging chromosomes.

Misaligned Chromosomes are a Major Source of Chromosomal Instability in ... Biology Diagrams
We find that MCAK is recruited to centromeres, kinetochores and chromosome arms in mid-meiosis I, and that MCAK depletion, or inhibition using a dominant-negative construct, causes chromosome misalignment. However, the majority of oocytes complete meiosis I and the resulting eggs retain the correct number of chromosomes.

CENP-E depletion disrupts the recruitment of key checkpoint proteins, including BubR1, Bub1, KIF2C, and Aurora B, indicating a causal relationship between chromosome misalignment and spindle assembly checkpoint activation in spermatogonia. Our findings demonstrate that CENP-E regulates kinetochore-m …

Micronuclei from misaligned chromosomes that satisfy the spindle ... Biology Diagrams
Finally, we describe new developments in our understanding of the immediate consequences of chromosome mis-segregation on the genome stability of daughter cells.