Targeting mTOR and Metabolism in Cancer Biology Diagrams The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) integrates nutrient and mitogen signals to regulate cell growth (increased cell mass and cell size) and cell division. The immunosuppressive drug rapamycin inhibits cell cycle progression via inhibition of mTOR; however, the signaling pathways by which mTOR r … In all eukaryotes, the target of rapamycin (TOR) signalling pathway couples energy and nutrient abundance to the execution of cell growth and division, owing to the ability of TOR protein kinase
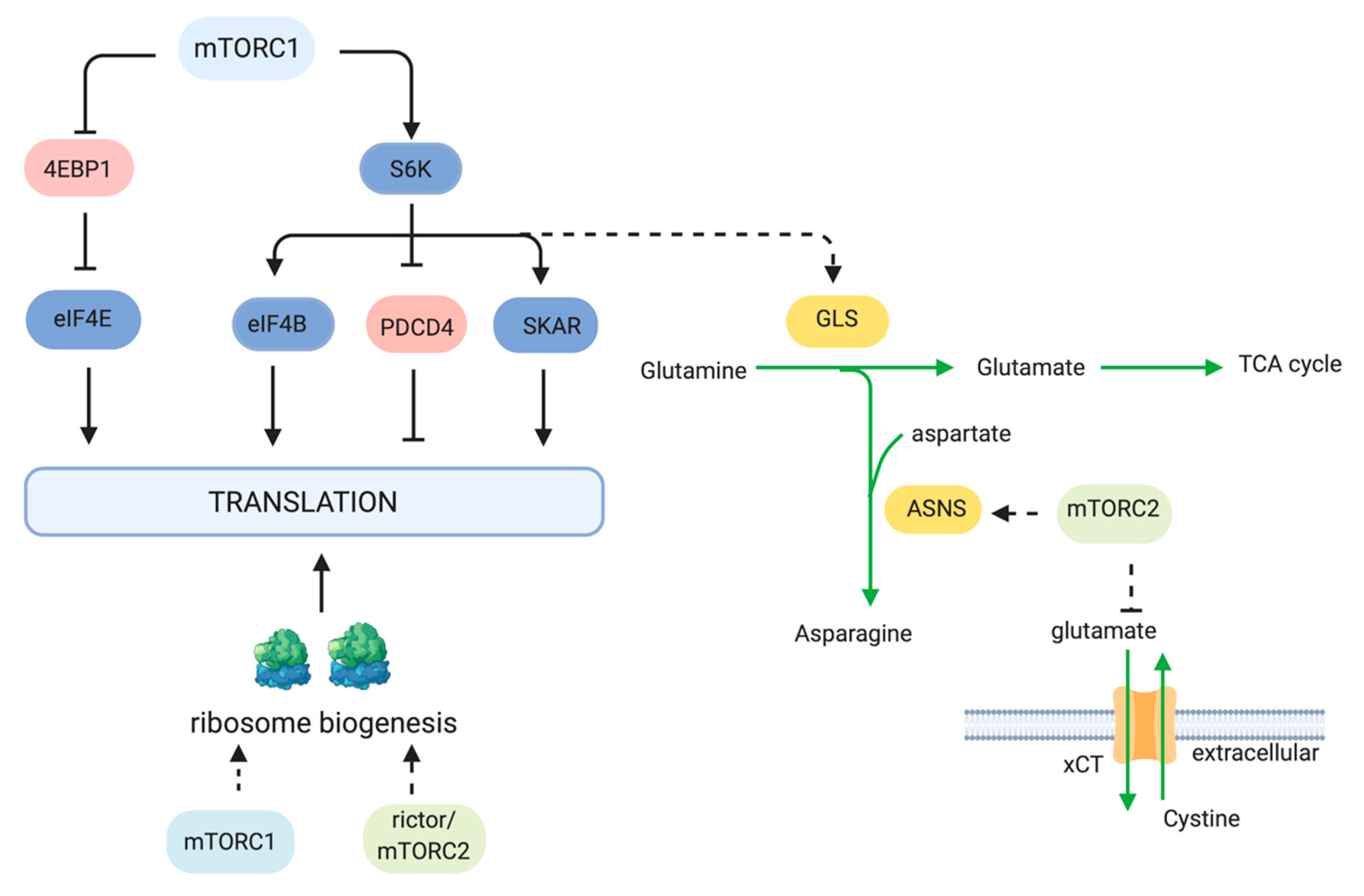
The mechanistic Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) coordinates eukaryotic cell growth and metabolism with environmental inputs including nutrients and growth factors. Extensive research over the past two decades has established a central role for mTOR in
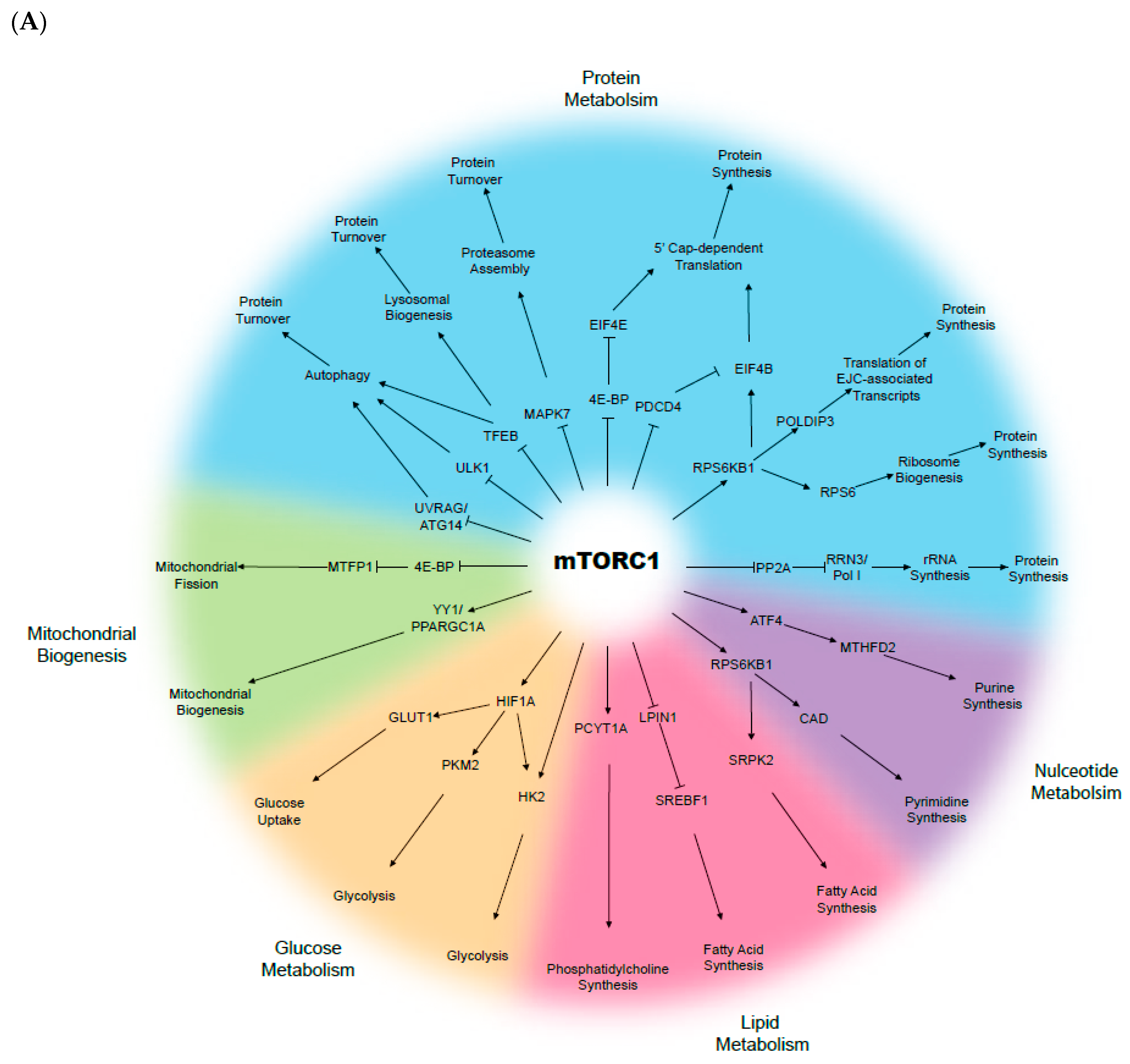
mTOR at the nexus of nutrition, growth, ageing and disease Biology Diagrams
The mechanistic/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) plays a master role in cell proliferation and growth in response to insulin, amino acids, energy levels, and oxygen. mTOR can coordinate upstream signals with downstream effectors, including transcriptional and translational apparatuses to regulate fundamental cellular processes such as energy utilization, protein synthesis, autophagy, cell
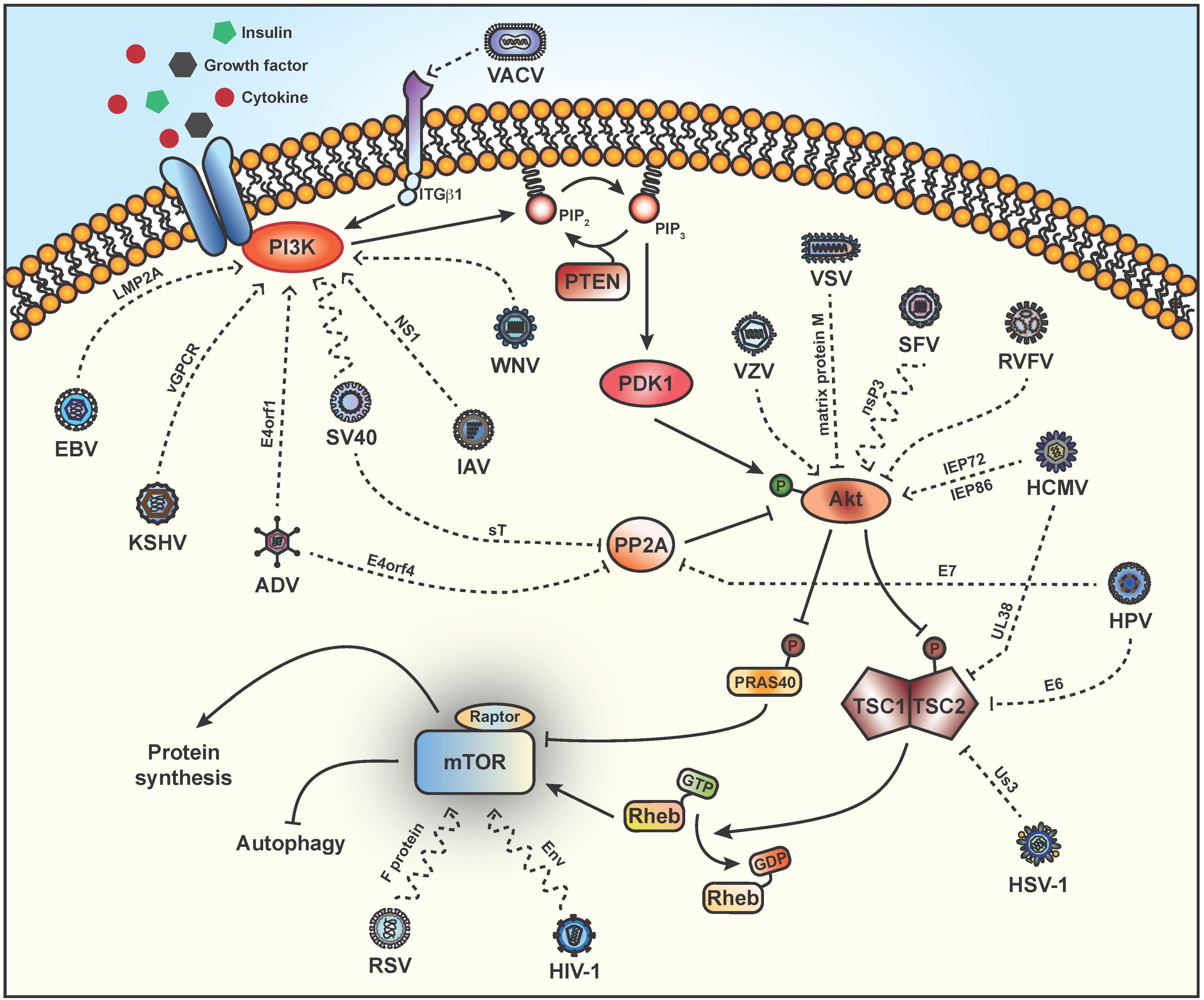
The mTOR pathway integrates a diverse set of environmental cues, such as growth factor signals and nutritional status, to direct eukaryotic cell growth. Over the past two and a half decades
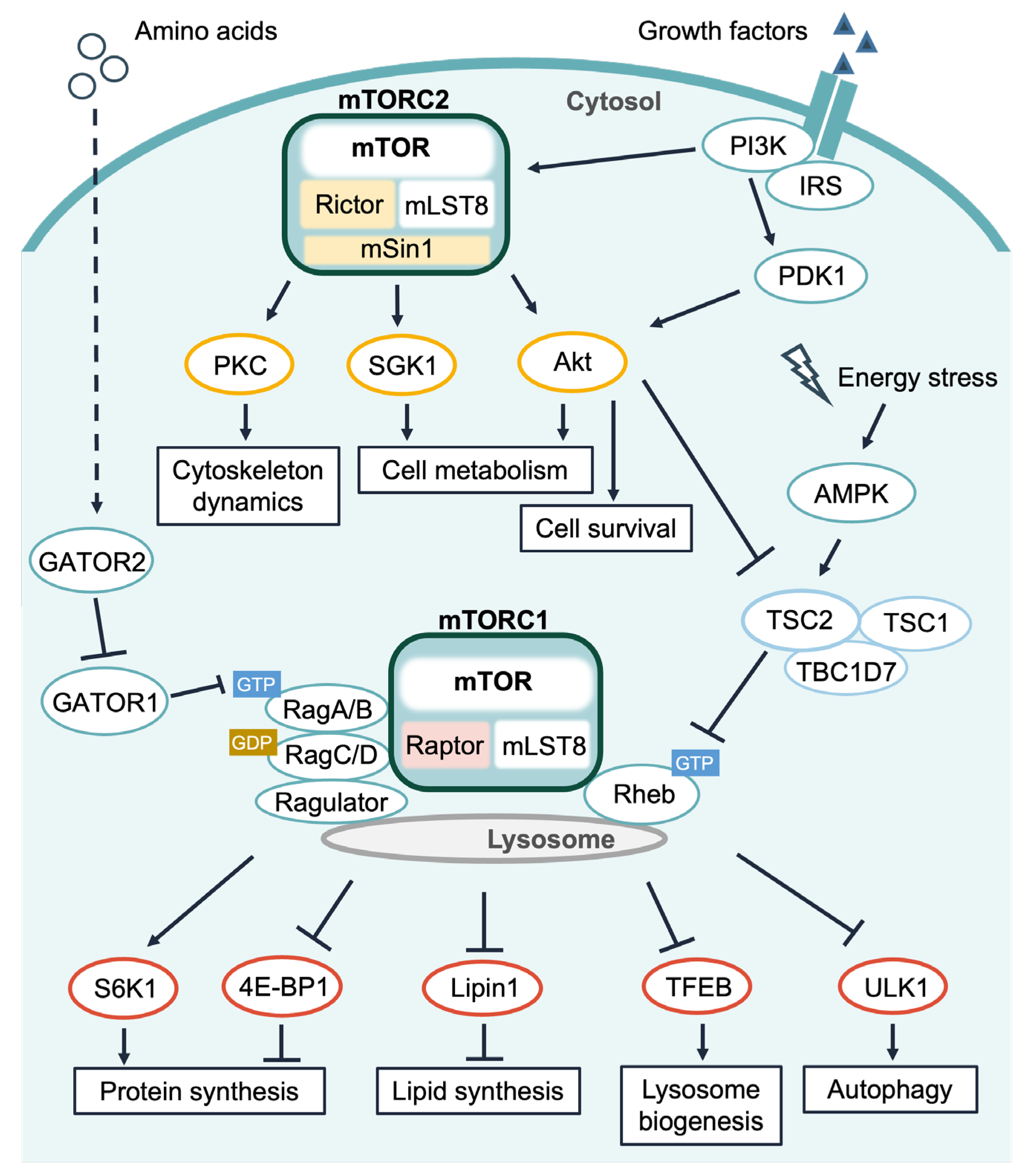
The mTOR Signaling Pathway: Key Regulator and Therapeutic Target for ... Biology Diagrams
The mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway senses and integrates a variety of environmental cues to regulate organismal growth and homeostasis. The pathway regulates many major cellular processes and is implicated in an increasing number of pathological conditions, including cancer, obesity, type 2 diabetes, and neurodegeneration. Here, we review recent advances in our The mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) coordinates eukaryotic cell growth and metabolism with environmental inputs, including nutrients and growth factors. we provide an overview of our current understanding of the mTOR pathway and its role in growth, metabolism, and disease. mTORC1 and mTORC2. mTOR is a serine/threonine protein kinase
