sister chromatid segregation Biology Diagrams Advanced techniques allow researchers to observe sister chromatids' structure and behavior. Fluorescence microscopy uses dyes to visualize chromatids in live cells, while G-banding provides detailed chromosomal views. Confocal and super-resolution microscopy enhance visualization, and CRISPR-Cas9 tagging allows precise chromatid observation. Takahashi and Hirota preview work from Stanyte et al. examining the behavior of sister chromatids and their resolution as the cell cycle progresses. Dynamic organization of sister chromatids after replication. Replicated chromatin fibers are highly mobile and readily dissociate from each other for >300 nm, beyond the achievable resolution

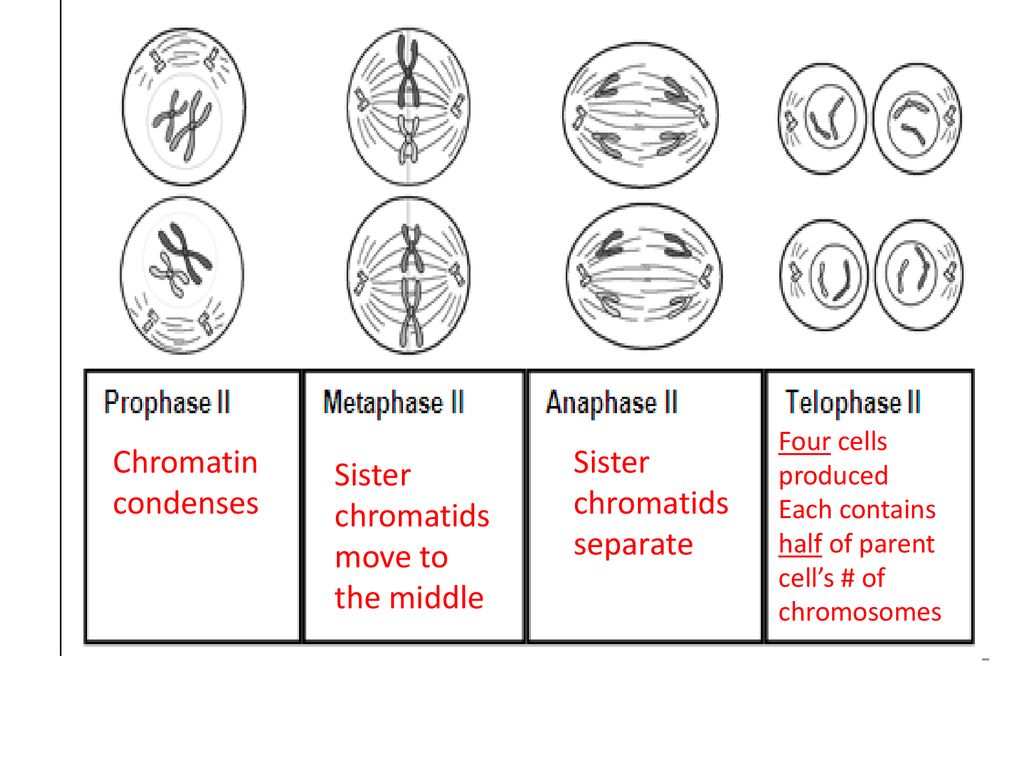
Centromere behavior also differs. In Anaphase I, cohesin proteins keep sister chromatids together, protected by Shugoshin. In Anaphase II, this protection is lost, allowing separase to cleave cohesin. The centromeres split, enabling chromatids to move independently. Errors and Resulting Consequences If this process were essential for sister chromatid separation, one would expect to find cdc5 mutants that block anaphase initiation. Consistent with this possibility, in Drosophila, there are polo mutants that arrest in metaphase with unseparated sister chromatids (Donaldson et al., 2001). Whether this metaphase arrest can be attributed to a Understanding the behavior of sister chromatids in mitosis is essential for grasping how cells divide and reproduce. Prophase. In prophase, the chromosomes condense and become visible under a microscope. Each chromosome appears as two sister chromatids joined at the centromere. The nuclear membrane starts to break down, and the mitotic spindle

Linking Chromosome Duplication and Segregation via Sister Chromatid ... Biology Diagrams
The paternal (blue) chromosome and the maternal (pink) chromosome are homologous chromosomes.Following chromosomal DNA replication, the blue chromosome is composed of two identical sister chromatids and the pink chromosome is composed of two identical sister chromatids.In mitosis, the sister chromatids separate into the daughter cells, but are now referred to as chromosomes (rather than
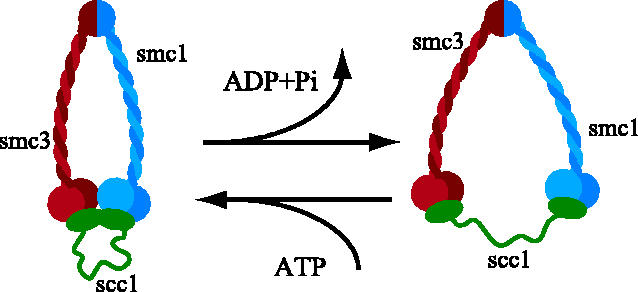
Previously, differential labeling of sister chromatids and their quantitative analysis of nonoverlapping volume indicated that the resolution between the sisters can be detected as soon as cells initiate mitosis, and it proceeds hand in hand with chromatin compaction through prophase (Nagasaka et al., 2016).Being based on volumetric analyses, however, this study was inapplicable for analyzing While sister chromatids are exact copies of each other, non-sister chromatids come from homologous chromosomes. They code for the same genes, but are not genetically identical. domain contains a dynamic arrangement of proteins that are involved in mitotic checkpoints and regulators of chromosome behavior.