Serotonin Pathway In Brain Photograph by Pikovit Science Photo Biology Diagrams It can signal to our brains when we're full, helping to prevent overeating. In the gut, where most of our body's serotonin resides, it aids in digestion and helps maintain gut motility. For example, serotonin interacts closely with Dopamine Production in the Brain: Pathways S. N. (2007). How to increase serotonin in the human brain An alternate pathway for serotonin exists in the pineal gland; it converts to melatonin. Serotonin originating from enterochromaffin cells is released into the portal circulation and undergoes rapid elimination from the plasma by way of uptake into platelets and liver metabolism. An estimated 90% of the serotonin in the human body is stored Serotonin, or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), is a neurotransmitter with an integral physiological role in the human body; it regulates various activities, including behavior, mood, memory, and gastrointestinal homeostasis.[1][2] Serotonin is synthesized in the raphe nuclei of the brainstem and the enterochromaffin cells of the intestinal mucosa.[3][4]
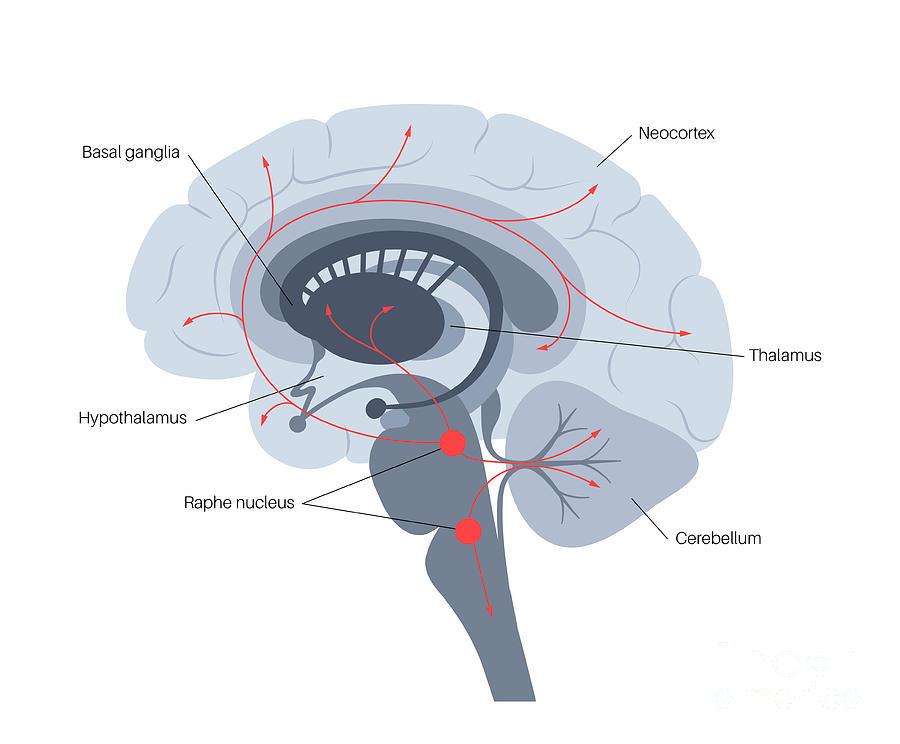
Serotonin (/ ˌ s ɛr ə ˈ t oʊ n ɪ n, ˌ s ɪər ə-/) [6] [7] [8] or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter.Its biological function is complex, touching on diverse functions including mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and numerous physiological processes such as vomiting and vasoconstriction. [9]Serotonin is produced in the central nervous system (CNS New findings reveal that the brain's serotonin system - which regulates everything from our moods to our movements - is made up of multiple parallel pathways that affect the brain in

The Expanded Biology of Serotonin Biology Diagrams
Serotonin acts as both a neurotransmitter and as a peripheral hormone. However, most 5-HT production occurs in the enterochromaffin (EC) cells of the intestinal mucosa. The gut is the largest endocrine organ in human body, and it produces almost 95% of all the serotonin.

Serotonin is a chemical that carries messages between nerve cells in the brain and throughout your body. Serotonin plays a key role in such body functions as mood, sleep, digestion, nausea, wound healing, bone health, blood clotting and sexual desire. Serotonin levels that are too low or too high can cause physical and psychological health Roughly95%of total body serotonin is released into the gut by intestinal enterochromaffin cells , but serotonin is involved at the very moment that food enters the body. Activation of taste-bud cells on the tongue causes serotonin release onto sensory afferent nerves ( 59 ) that transmit taste information to the CNS.
