Beetles and their biodiversity in dead wood Biology Diagrams Some species of beetles even feed on decaying material, such as dung, dead leaves, and dead wood. Beetles can also be scavengers, consuming any food they come across in their environment. What is a Beetle? Beetles are one of the most abundant and diverse groups of organisms on the planet, with over 350,000 species identified. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like 1) In the food chain 'grass --> grasshopper --> frog --> snake --> eagle', what organism is the primary consumer?, 1) In the food chain 'grass --> grasshopper --> frog --> snake --> eagle', what organism is the producer?, Which of the following links of the food chain eats decaying matter? and more.

The insect food chain is a complex network of interconnected organisms, each playing a vital role in the ecosystem. Plants, as producers, convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis. Herbivores (primary consumers) feed on plants, while carnivores (secondary consumers) hunt and eat herbivores. At the top of the food chain, apex predators control populations of other animals. In the food chain, beetles occupy crucial positions, acting as primary consumers, secondary consumers, scavengers, and decomposers within habitats like rotten logs, which support a diverse range of organisms. Common scavengers such as sow bugs, carpenter ants, bark beetles, and termites burrow through decaying wood, further aiding decomposition.
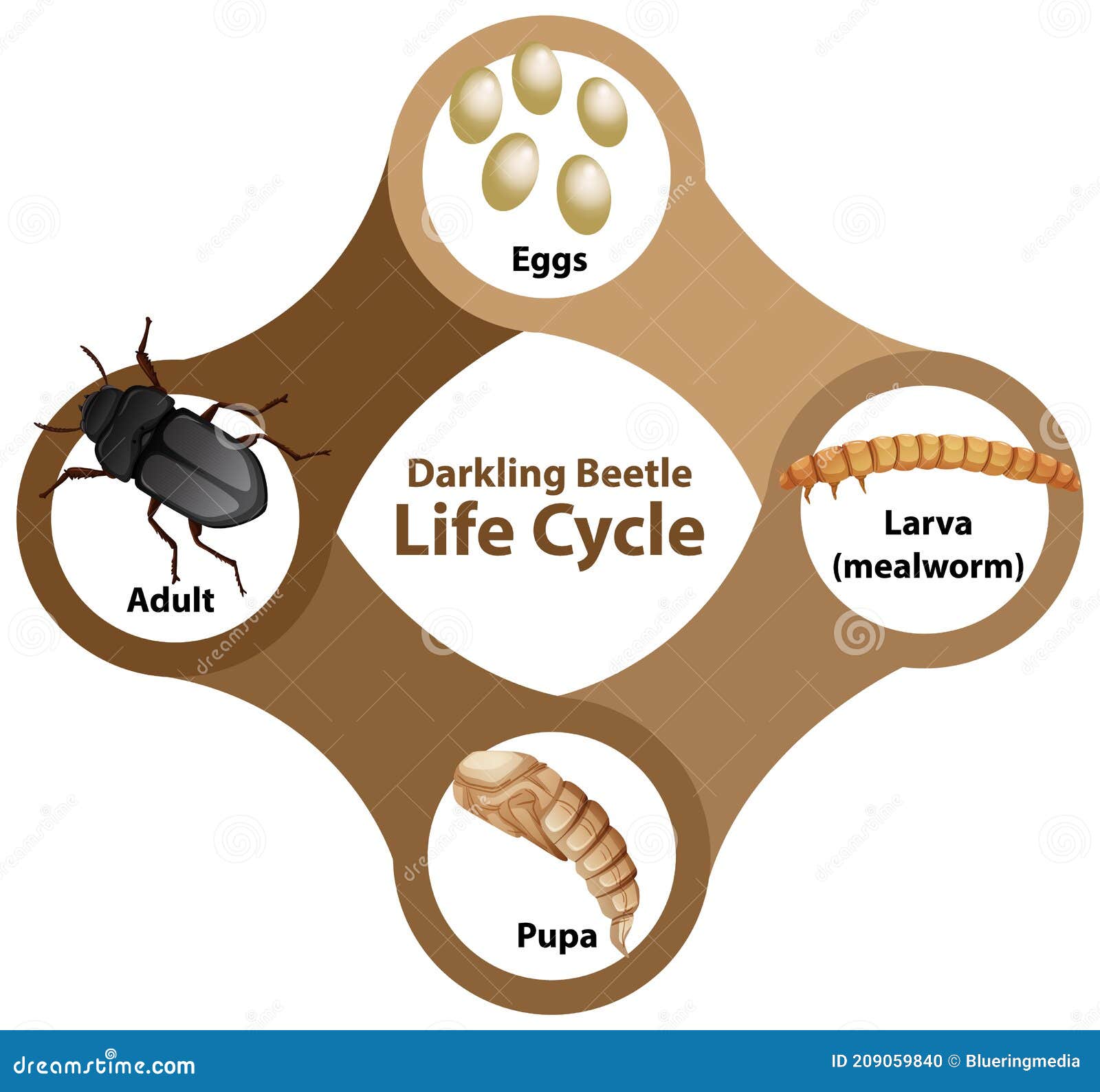
What Does a Beetle Eat? (Surprising Facts Revealed) Biology Diagrams
In a field with many green plants, a food chain begins. First, insects eat the plants. Then, rats eat the insects. After that, snakes eat the rats, and birds eat the snakes. When the birds die, decomposers break them down. as it involves organisms that break down and feed on decaying plants, animals, and other organic material. The main food of grubs is roots. They also eat decaying organic material, wood, fungi and animal droppings. Different grubs have different preferences for food based on habitat, life cycle, and mandible shape. By destroying the root system, root-feeding grubs may damage lawns, gardens, and crops. The role of grubs in the environment is important.

Food Chains A food chain represents a single pathway through which energy and matter flow through an ecosystem. An example is shown in Figure 9.19. Food chains are generally simpler than what really happens in nature. Most organisms consume—and are consumed by—more than one species. Figure 9.19: This food chain includes producers and

Create a food chain. Choose the biotic factors from the list and move ... Biology Diagrams
This leaves holes that can help the log break down and become food for other creatures faster. The larvae of some beetle species, like the longhorn beetle, feed on decaying wood. In some species, the larvae eat soft decayed wood. In other species, like the bess beetle, the parents chew the wood to make it soft enough for the larvae to eat.
