Alchetron The Free Social Encyclopedia Biology Diagrams Unsurprisingly, mitotic exit control pathways are integrated with numerous other aspects of the cell division cycle. For example, checkpoints monitoring spindle assembly, DNA damage, completion of replication, and even bud neck morphogenesis, impinge on the M/G1 transition. While this chapter necessarily focuses on pathways that underlie

Interestingly, activation of spindle checkpoints inhibits Bfa1p phosphorylation, suggesting that these signaling pathways prevent mitotic exit by maintaining the GAP activity of Bub2p/Bfa1p. Main Text. Maintaining genomic integrity requires high fidelity of chromosome segregation during mitosis. This is ensured by intrinsic properties of the
Mitotic Exit and Separation of Mother and Daughter Cells Biology Diagrams
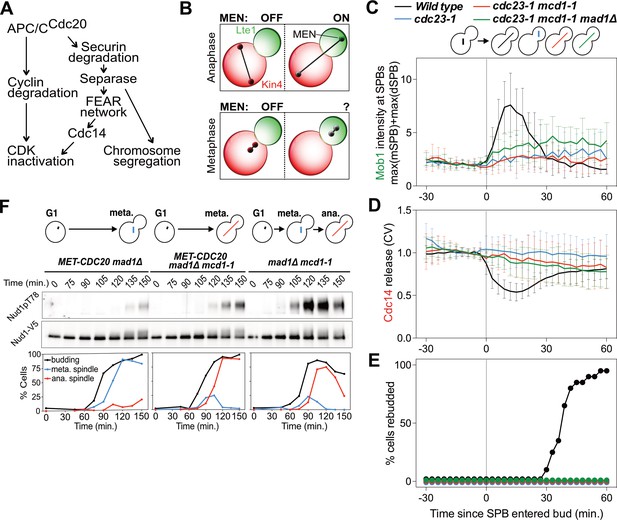
In budding yeast, the Mitotic Exit Network (MEN) is a signaling pathway known to drive cells out of mitosis and promote the faithful division of cells. The MEN triggers inactivation of cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk1), the master regulator of mitosis, and the onset of cytokinesis after segregation of …
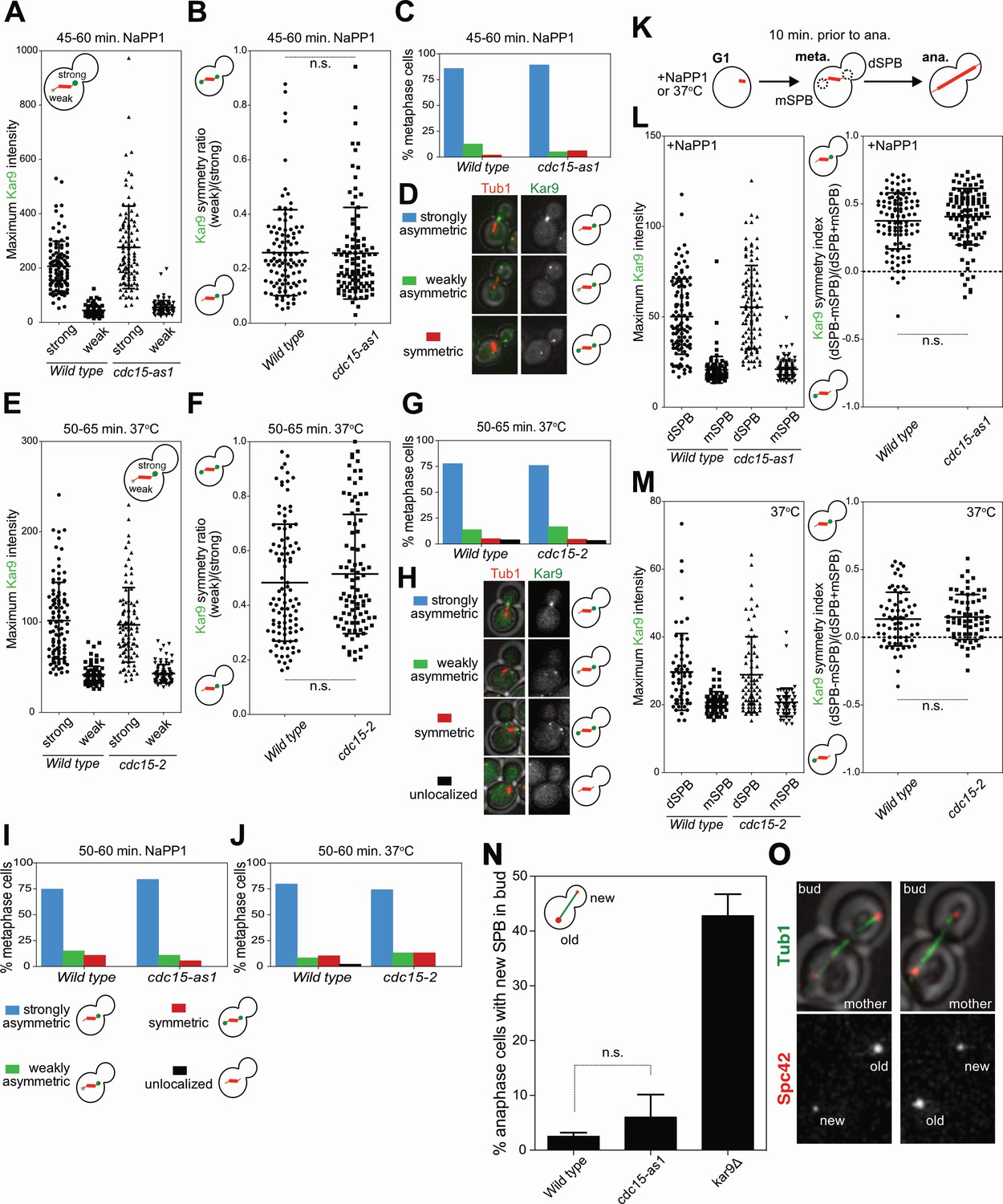
In budding yeast, the Mitotic Exit Network (MEN) is a signaling pathway known to drive cells out of mitosis and promote the faithful division of cells. The MEN triggers inactivation of cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk1), the master regulator of mitosis, and the onset of cytokinesis after segregation of the daughter nuclei.

The Mitotic Exit Network: new turns on old pathways Biology Diagrams
Cdc14 is the ultimate effector for a complex signal transduction pathway known as the 'mitotic exit network', or MEN 2., 3. (Fig. 1). This pathway is activated after nuclear partitioning by the Ras-like GTPase Tem1, which triggers a protein kinase cascade comprising Cdc15, Dbf2/20 and Mob1, a protein of unknown function [4]. Mitotic exit is an important transition point that signifies the end of mitosis and the onset of new G1 phase for a cell, and the cell needs to rely on specific control mechanisms to ensure that once it exits mitosis, it never returns to mitosis until it has gone through G1, S, and G2 phases and passed all the necessary checkpoints. Many factors including cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases
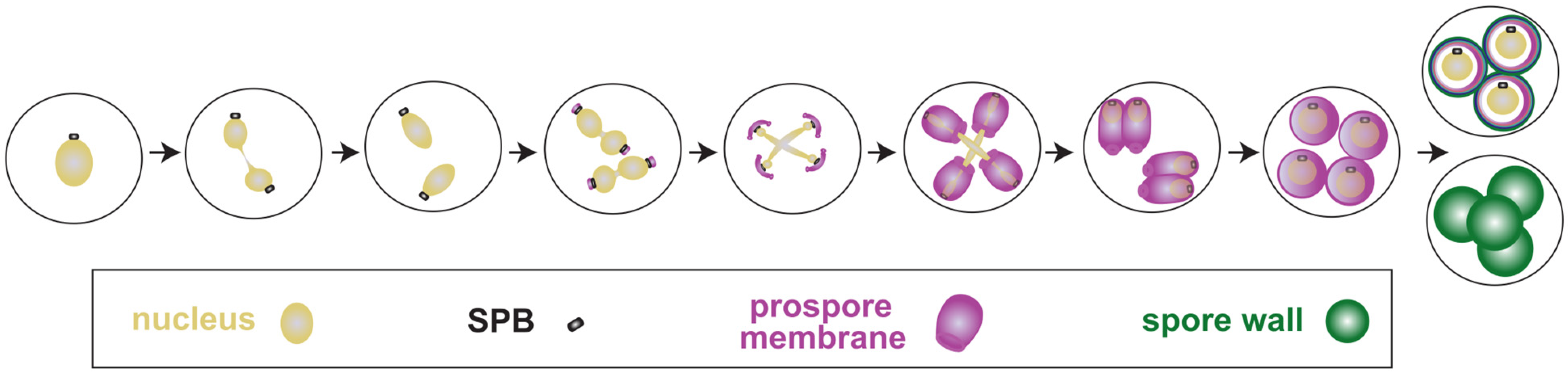
Mitotic exit is characterized by mitotic spindle breakdown, chromosome decondensation and reassembly of interphase structures, particularly the NE. Perhaps significantly though, perturbation of the mitotic exit pathway in some strains of budding yeast prevents cytokinesis but not nuclear division [76]. This key issue aside, the comparative Fundamentally, the mitotic-exit system, which includes the Cdc14 early anaphase release (FEAR) and mitotic-exit network (MEN) pathways, has relatively simple functionality. Yet an intricate complex control system has evolved to make the basic functions robust and precise under a variety of circumstances. From an engineering perspective, the In budding yeast, the Mitotic Exit Network (MEN) is a signaling pathway known to drive cells out of mitosis and promote the faithful division of cells. The MEN triggers inactivation of cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk1), the master regulator of mitosis, and the onset of cytokinesis after segregation of the daughter nuclei.
